As featured on IoT Agenda.
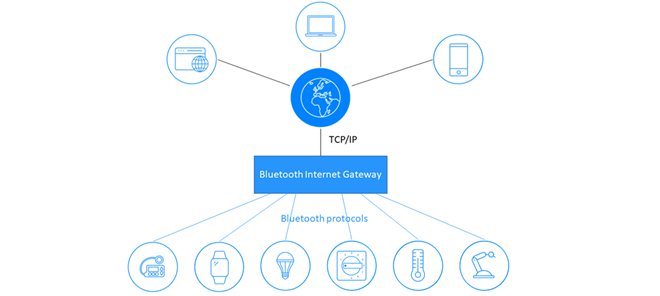
Mesh networking is key to the success of the Internet of Things (IoT). In comparison to traditional wired counterparts, mesh networks are less expensive to implement, more adaptable and scalable, and offer greater reliability for high-traffic implementations. While niche technologies such as Thread and ZigBee have standardized mesh support, a limited install base and unpredictable performance, reliability, scalability, and interoperability have created challenges for an industrial-grade technology to emerge for large-scale mesh networking scenarios like building automation.

How Bluetooth Mesh Measures Up
In contrast, Bluetooth® Mesh, released in July 2017, was specifically designed to address the unique requirements of commercial and industrial networks, and offers a wider range of applications than current technologies. In a recent whitepaper, Ericsson tested the capabilities of Bluetooth Mesh and its ability to provide the unique features that commercial industries require. The goal of this test was to illustrate the impact of configuration and deployment strategies on a Bluetooth Mesh network to determine if thousands of nodes could potentially communicate with no single point of failure, and guarantee interoperability. Specifically, Ericsson looked at the managed flooding communication model of Bluetooth mesh.
Ericsson describes managed flood as a message relay technique in which “all nodes are asynchronously deployed and can talk to each other directly. After provisioning them, the network simply starts working and does not require any centralized operation — no coordination is required and there is no single point of failure. A group of nodes can be efficiently addressed with a single command, making dissemination and collection of information fast and reliable.” This approach offers flexibility in deployment and operation.
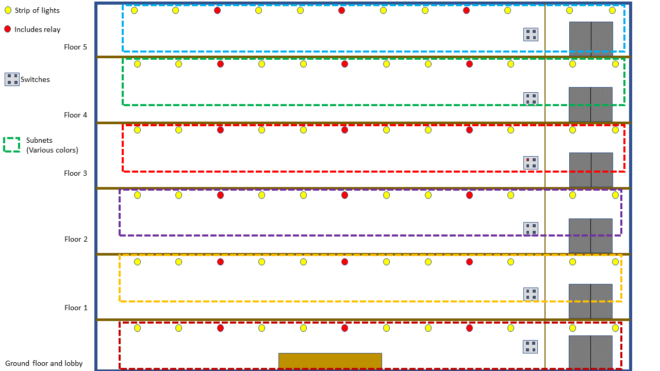
Using a capillary network, Ericsson executed a large-scale building automation test case and full-stack implementation of Bluetooth Mesh in a system-level simulator to determine if there should be any concern around high congestion, which may result in packet loss for contention-based access in the unlicensed spectrum. This office automation scenario included a total of 879 devices, including window sensors, occupancy sensors, HVAC sensors and actuators, light switches, and lightbulbs, all deployed in an area of 2,000 square meters. The network performance evaluation was based on three traffic setups in the evaluation: a low-traffic case with aggregate application throughput of ~150 bps, a medium-traffic case with aggregate application throughput of ~1 Kbps, and a high-traffic case with aggregate application throughput of ~3 Kbps.

Quality of Service
The most crucial performance metric of any mesh network is the quality of service (QoS), which Ericsson defines as the ratio of transmitted packets that reach the end destination within human perceivable time (300 milliseconds in this case, which is a typical requirement for lighting applications). The QoS of the Bluetooth® Mesh network went up to an expected level of >99.9 percent for five out of the six tested cases and up to 99.1 percent for the final dense relay deployment with high traffic. In all cases, all endpoints were reached within the 300-millisecond delay. Overall, Ericsson saw the best performance when deploying six relays every 1,000 square meters, corresponding to roughly 1.5 percent of the total number of nodes.
Ericsson concluded that, with proper deployment and configuration of relevant parameters of the protocol stack, Bluetooth Mesh supports the operation of dense networks with thousands of devices, overcoming any initial concerns regarding high congestion. Ericsson also argued that Bluetooth, with the release of the Bluetooth Mesh Specification, is a strong candidate to become the dominant short-range technology to connect edge nodes in a capillary network that uses short-range radio-access technologies to provide groups of devices with wide-area connectivity.
Standardized and Interoperable by Design
As Ericsson explained in the whitepaper, “Bluetooth Mesh is standardized and interoperable by design. Qualification and interoperability testing is rigorous and involves all aspects of the protocol stack, including security. There is no risk of companies developing separate processes for different parts of the stack. Moreover, the specifications are open and can be tested by the community.” This, coupled with the larger Bluetooth footprint, as well as the value-added capabilities of Bluetooth technology for providing localized information, asset tracking, way-finding services, and more, gives Bluetooth mesh the potential to be quickly adopted by the market.

![shutterstock 1653733096[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/shutterstock_16537330961-660x372.jpg)
![Periodic Advertising with Responses[1]](https://www.bluetooth.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Periodic-Advertising-with-Responses1-660x345.png)